
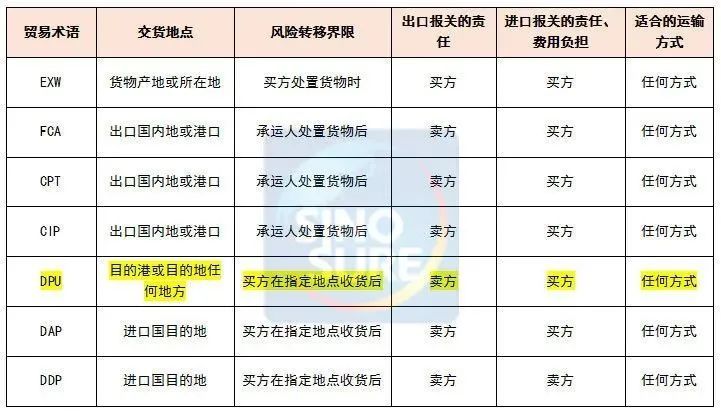
EXW/FCA/CPT/CIP/DPU/DAP/DDP:2020 Incoterms.
Release time:
2020-09-30 14:14
Source:
China Credit Insurance Small and Micro Enterprise Service WeChat Public Number
EXW
The full name of EXW is Ex Works(...named place), which means factory delivery (designated place) in Chinese. Means that the seller delivers the goods from the factory (or warehouse) to the buyer, unless otherwise specified, the seller is not responsible for loading the goods onto the car or ship arranged by the buyer, nor for export customs clearance. The buyer bears all costs and risks from the delivery of the seller's factory to the final destination.
The seller bears the least risk, liability and expense when closing in EXW terms. On the delivery side, the seller is only required to provide commercial invoices or electronic data and, if required by the contract, documents proving that the goods delivered are in conformity with the provisions of the contract.
FCA
The full name of FCA is Free Carrier(...named place), that is, the delivery carrier (designated place). It means that the seller delivers the goods that have been exported and cleared to the carrier designated by the buyer at the designated place to complete the delivery. In accordance with commercial practice, when the seller is required to cooperate with the carrier by entering into a contract, the seller may do so at the buyer's risk and expense.
In the old version, the delivery of the goods was completed before loading on board, and the carrier was obliged to issue a "shipped" bill of lading or a "received" bill of lading with notes on board, which would only be issued when the goods were actually loaded on board.
To address this issue, the FCA Incoterms®The 2020 provides a new option: the parties to the transaction can agree that the buyer will instruct its carrier to issue and deliver the bill of lading to the seller before loading the goods on board the ship. The shipping company and the seller are obliged to pass the bill of lading to the buyer through the bank channel. The ICC was aware of the market need, while noting a theoretical inconsistency between the point of delivery envisaged by the FCA provisions and the requirements of the bill of lading on board.
CPT
CPT term Carriage Paid to (...named place of destination) means cost plus freight to (designated destination), means that the seller hands over the goods to its designated carrier and must pay the freight to transport the goods to the designated destination, while the buyer bears all risks and other costs after delivery. The term applies to all modes of transport, including multimodal transport.
Comparison of CFR and CPT
The similarities between the two are: the seller arranges the carriage of the goods, pays the relevant freight, and handles the export formalities and submits the relevant documents.
The differences between the two are: first, the applicable modes of transport are different, CFR is only applicable to sea transport, which is port-to-port transport; CPT is applicable to various modes of transport (including container transport, multimodal transport, sea, land and air), which is door-to-door transport. Second, the location of delivery and risk transfer is different, CFR risk division to the port of shipment of goods on board the ship as the boundary, CPT to the delivery carrier as the boundary. Finally, the documents submitted are different. CFR provides a sea way bill of lading, which is a document of title, can be transferred and sold, and CPT usually provides intermodal documents, but only documents for the handover of goods, which cannot be transferred and cannot be sold. From the development trend, CPT has a tendency to replace CFR.
CIP
The full name of CIP is Carriage and Insurance Paid to (...named place of destination) Chinese means freight and insurance to (designated destination), which means that the seller hands over the goods to its designated carrier, pays the freight to transport the goods to the designated destination, and handles freight insurance for the buyer for the goods in transit, while the buyer bears all risks and other expenses after delivery. The writing form is "CIP designated destination". The CIP term applies to all modes of transport, including multimodal transport.
Changes in CIP insurance coverage in Incoterms2020:
CIP belongs to the buyer's insurance to invest in the highest risk (e. g. CIC all insurance and ICC(A) insurance), while the CIF term under the insurance requirements remain unchanged, still invest in the lowest risk can be.
DPU
* In the Incoterms2020, DAT is changed to DPU, the place of delivery of the DPU term.
The full name of DPU is Delivered at Place Unloaded, which means terminal delivery in Chinese. It means that the seller delivers the goods to the buyer after unloading at the designated destination or port of destination, and the seller bears all risks and costs of transporting the goods to the seller at the designated destination or port of destination, except for import costs. It is still the destination, but this destination is no longer limited to the end of the transport, but can be anywhere.
DAP
The full name of DAP is Delivered At Place(named place of destination), that is, destination delivery (designated destination). When using DAP terminology to conclude a transaction, the seller shall be responsible for handing over the goods stipulated in the contract to the buyer for disposal within the specified period of time according to the usual route and usual way, I .e. to complete the delivery, and the seller shall bear all risks of transporting the goods to the designated place.
DDP
The full name of DDP is Delivered Duty Paid (... named place of destination), I .e. after-duty delivery (... designated destination), the seller completes customs clearance at the designated destination and places the goods that have not yet been unloaded on the means of transport for delivery at the buyer's disposal, I .e. delivery is completed. The seller bears all risks and costs of transporting the goods to the destination, including any import taxes and fees payable at the destination when customs formalities are required.
The DDP term is one of the 11 trade terms in which the seller bears the greatest responsibility and bears the most cost, which means that the seller, at the designated destination, goes through import clearance procedures and delivers the goods that have not yet been unloaded on the means of transport at the place of delivery to the buyer to complete the delivery. The seller must bear all risks and costs of transporting the goods to the designated destination, including any "taxes" payable at the destination when customs formalities are required (including the responsibility and risk of customs formalities, as well as the payment of fees, duties, taxes and other fees). This term should not be used if the seller is unable to obtain, directly or indirectly, an import licence. However, if the parties wish to exclude from the seller's obligations all costs to be paid for the import (e. g. VAT), they should be clearly stated in the contract of sale. The term applies to all modes of transport.
Trade
